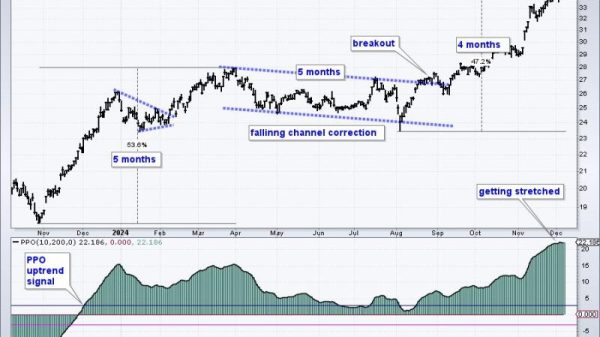
Gold has long been considered a safe haven asset, often used by investors as a hedge against economic uncertainty and market volatility. In times of geopolitical turmoil or economic instability, gold tends to maintain its value, making it an attractive option for those seeking to protect their wealth. With the ever-changing landscape of the global economy, understanding how to use gold investments effectively as a hedge remains crucial for investors looking to mitigate risks and secure their portfolios.
One key way to utilize gold as a hedge is through physical ownership of the precious metal. Owning physical gold in the form of bullion, coins, or bars allows investors to directly benefit from the metal’s intrinsic value. In times of crisis, physical gold can serve as a store of value that is not contingent on the performance of other assets, providing a tangible hedge against inflation and currency devaluation.
Another popular method of using gold as a hedge is through gold-backed exchange-traded funds (ETFs). These investment vehicles offer investors exposure to the price of gold without the need for physical ownership. ETFs such as SPDR Gold Shares (GLD) and iShares Gold Trust (IAU) track the price of gold and enable investors to easily buy and sell shares, providing a liquid and cost-effective way to gain exposure to the precious metal.
Furthermore, gold mining stocks can also be utilized as a hedge against market volatility. While gold mining stocks are influenced by factors beyond the price of gold, such as production costs and operational efficiency, they tend to exhibit a positive correlation with the price of gold. Investing in gold mining companies can offer leverage to the price of gold, potentially resulting in higher returns during periods of increasing gold prices.
Derivatives, such as gold futures and options, provide another avenue for investors to hedge their portfolios with gold. By entering into futures contracts or options agreements linked to the price of gold, investors can protect against adverse price movements while maintaining the potential for profit. However, derivatives come with their own set of risks and complexities, requiring a thorough understanding of the market and careful risk management.
In conclusion, gold remains a valuable asset for investors seeking to hedge against economic uncertainty and market volatility. Whether through physical ownership, ETFs, gold mining stocks, or derivatives, there are various ways to incorporate gold investments into a diversified portfolio as a hedge. By understanding the different methods available and their respective pros and cons, investors can effectively utilize gold to protect their wealth and navigate turbulent financial environments.