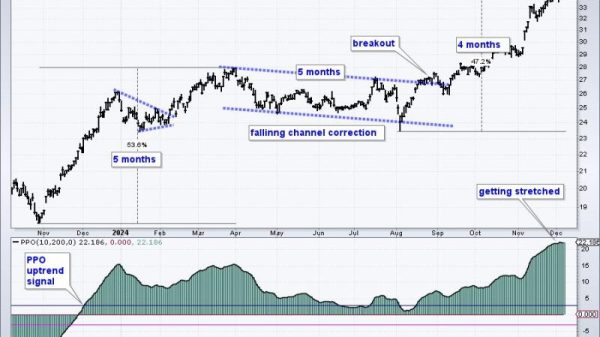
Inflation Rate Falls to 2.9% in July, Adding to Signs that Surging Prices have Abated
The inflation rate in July showed a decrease, reaching 2.9%, which is a positive indicator that the surge in prices may have abated, according to recent reports. This decline follows a period of concern over rapidly rising prices that impacted consumers and businesses alike. Various factors have contributed to this decrease and provide hope for a more stabilized economic outlook in the coming months.
One of the key factors driving the decrease in the inflation rate is the easing of supply chain disruptions that had previously led to shortages and increased prices for various goods and services. As global supply chains gradually recover from the disruptions caused by the pandemic, the availability of products has improved, leading to a more balanced supply-demand dynamic.
Additionally, government interventions and monetary policies have played a significant role in controlling inflation. Central banks around the world have implemented measures to curb inflationary pressures, such as adjusting interest rates and scaling back stimulus programs. These actions have helped to moderate price increases and bring inflation down to a more manageable level.
Furthermore, the stabilization of energy prices has also contributed to the decline in the inflation rate. The volatility in oil and gas prices, which had been a major factor driving inflation higher, has subsided in recent months. This stability has provided relief to businesses and consumers, as energy costs are a significant component of overall price levels.
On the consumer side, the decrease in inflation is likely to have a positive impact on purchasing power and consumer sentiment. With prices stabilizing or even decreasing for certain goods and services, consumers may feel more confident in their spending and be encouraged to make purchases. This, in turn, could stimulate economic growth and contribute to a more robust recovery.
Looking ahead, it will be crucial for policymakers to continue monitoring inflation and implementing appropriate measures to prevent a resurgence of price pressures. While the current decrease in inflation is a positive development, it is essential to ensure that price levels remain stable and do not veer into deflationary territory.
In conclusion, the recent decline in the inflation rate to 2.9% in July is a promising sign that the surge in prices may have abated. Factors such as easing supply chain disruptions, government interventions, and stabilized energy prices have all contributed to this positive trend. By staying vigilant and proactive in addressing inflationary pressures, policymakers can help maintain a healthy economic environment for businesses and consumers alike.