The Boeing Starliner’s Strange Test Flight is Finally Returning to Earth, But It’s Empty
Background
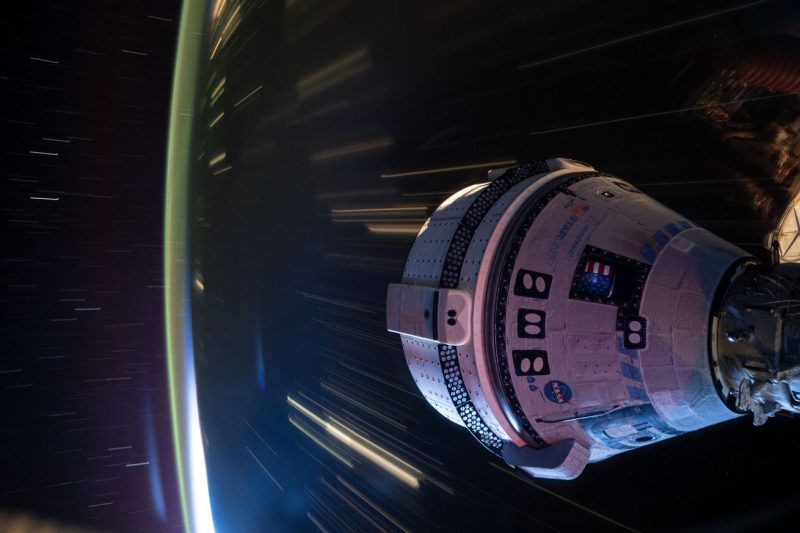
The Boeing Starliner, a spacecraft designed for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, recently embarked on a test flight to demonstrate its capabilities for transporting astronauts to the International Space Station (ISS). However, the mission took an unexpected turn when technical issues prevented the spacecraft from reaching its intended orbit, leaving it in a lower orbit than planned.
Reasons for Aborting the Mission
The decision to abort the mission and bring the Starliner back to Earth was made after it became clear that the spacecraft would not be able to reach the ISS as originally planned. Several factors contributed to this decision, including a timing error that caused the spacecraft’s thrusters to consume more fuel than anticipated, jeopardizing its ability to safely dock with the ISS.
Significance of the Test Flight
Despite the mission’s failure to achieve its primary objective, the test flight provided valuable data that will help engineers at Boeing and NASA understand what went wrong and how to prevent similar issues in future missions. This incident underscores the complexity and challenges of space travel, emphasizing the importance of thorough testing and preparation.
Lessons Learned
The Boeing Starliner’s test flight serves as a reminder of the inherent risks involved in space exploration and the need for rigorous testing and contingency planning. By analyzing the root causes of the mission’s failure, engineers can identify areas for improvement and implement corrective actions to ensure the safety and success of future missions.
Future of the Boeing Starliner Program
Despite the setback experienced during this test flight, Boeing remains committed to the success of the Starliner program. The company will continue to work closely with NASA to address the issues that led to the mission’s early termination and make necessary adjustments to ensure the spacecraft’s readiness for future crewed missions to the ISS.
Conclusion
The Boeing Starliner’s test flight may not have gone as planned, but it has provided valuable insights that will inform the program’s future development. By learning from this experience and applying the lessons gained, Boeing and NASA can strengthen the reliability and safety of the Starliner spacecraft, moving one step closer to realizing the goal of commercial crew transportation to low Earth orbit.